
Gout, renowned for its painful intrusion into joints, is often found on the verge of the debate: Is gout an autoimmune disease or a metabolic misalignment? Step into the realm of medical mysteries and explore the origin of gout, unraveling its classification as an autoimmune adversary or a metabolic disease. This piece of writing will help you navigate through the veils of every uncertainty about “GOUT” and assist you into ways to treat your condition.
Here you will discover some facts about gout, some factors that affect this condition, and a few profound treatments anyone can try. Let’s dive right in!
Is Gout An Autoimmune Disease? Unveiling The Relationship!
Gout, a form of inflammatory arthritis, is known for its painful and rather devastating effects on affected individuals. However, a question remains… Is gout an autoimmune disease or is it some other medical condition? Here are a few things you must learn to understand this relationship.
1. Understanding Gout
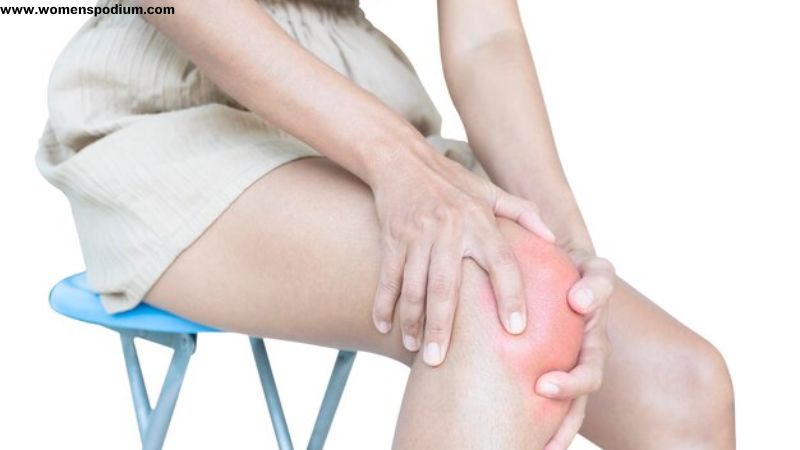
Gout is primarily characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, sometimes back pain, redness, and swelling in the joints, often affecting the big toe, though it can occur in other joints as well. These attacks are caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints and surrounding tissues, leading to inflammation.
2. Autoimmune Diseases
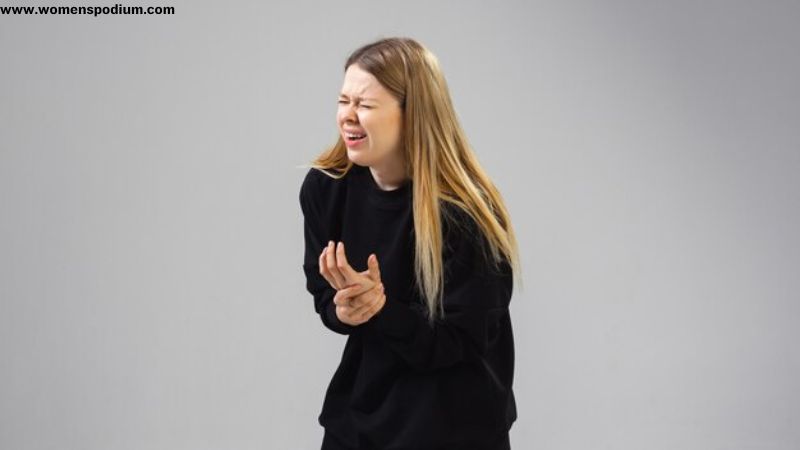

Autoimmune diseases occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its tissues, mistaking them as foreign or harmful. Common autoimmune diseases include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and psoriasis, among others. These conditions involve an immune response that targets healthy tissues, leading to inflammation and damage.
3. Is Gout an Autoimmune Disease?
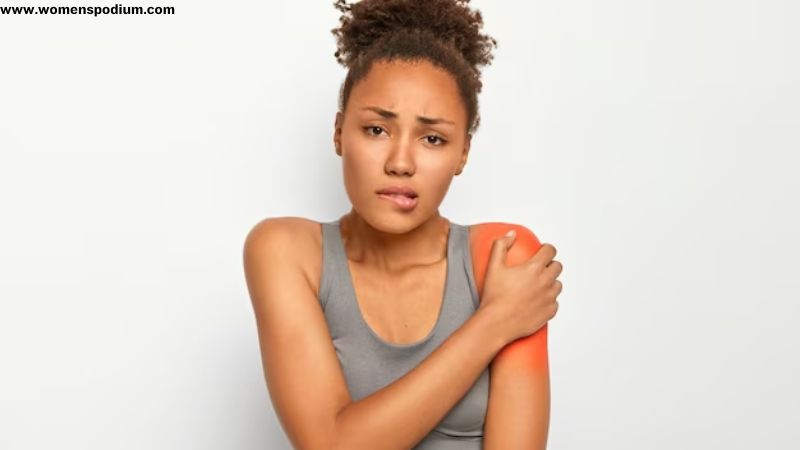

NO! Gout is not classified as an autoimmune disease. Unlike autoimmune conditions where the body’s immune system attacks its tissues, gout is primarily caused by the body’s inability to properly metabolize uric acid, leading to its accumulation and subsequent crystal formation in the joints.
4. Relationship with Inflammation
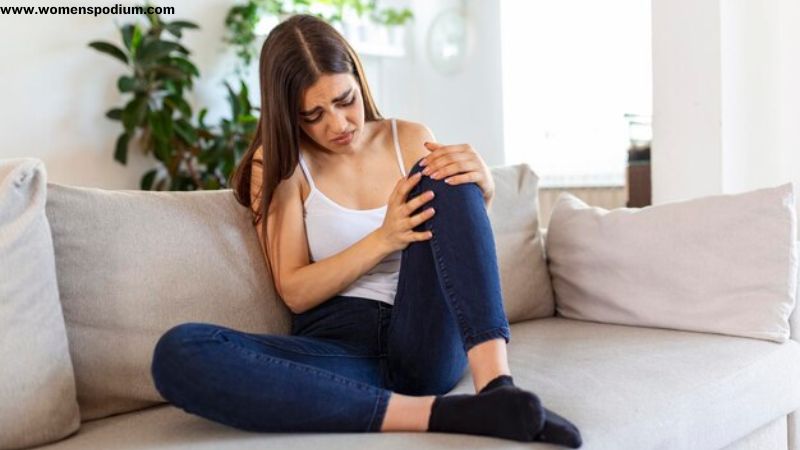

While gout isn’t an autoimmune disease, it does involve inflammation, which is a common aspect of autoimmune conditions. The body’s response to the presence of uric acid crystals in the joints leads to an inflammatory cascade and causes pain and swelling. Therefore, it is advised to have a proper anti-inflammatory diet plan as well.
Gout Triggers: The 5 Influential Factors Behind Severity Of Gout!
Several factors can influence the development, frequency, and severity of gout, a type of arthritis caused by the crystallization of uric acid in joints. These factors include:
1. Your Diet Choices

Regardless of the question; Is gout an autoimmune disease, one must avoid an unhealthy diet. Foods high in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, seafood, and certain vegetables (like asparagus and spinach), can increase uric acid levels in the body, triggering gout attacks. Beer and liquor, especially in excessive amounts, can elevate uric acid levels, leading to gout flares.
Also Read: Include some healthy foods in your diet or follow a vegetarian anti-inflammatory diet plan to start.
2. Genetics And Family History

A genetic predisposition to elevated uric acid levels or impaired excretion of uric acid by the kidneys can increase the likelihood of developing gout. Family history can significantly impact an individual’s susceptibility to the condition.
3. Some Medical Conditions

High blood pressure and obesity increase gout inflammation. Being overweight or obese can lead to higher levels of uric acid in the body. Therefore, you must know the right food intake for your body. Other health conditions, like hypertension or chronic kidney disease, can affect uric acid regulation in the body, increasing the risk of gout.
4. Your Daily Lifestyle

If your body is constantly dehydrated, you are at a higher risk of developing gout because of your body’s decreased ability to excrete uric acid. Lack of physical activities and exercise can lead to more uric acid accumulation and thus gout flare-ups.
5. The Age And Gender Factor

Gout is more common in men than in women, particularly occurring in men after the age of 30 and in women after menopause. Also, if you experienced gout attacks in the past, it increases the likelihood of recurrent gout flares.
The 6 Best Ways To Treat Gout And Enjoy Better Health
You got the answer to the question; Is gout an autoimmune disease? Now that you know it is a metabolic dysfunction, you should know how to treat it better. Here are seven ways to treat gout:
1. Choose Your Diet Wisely

Avoiding foods high in purines, such as red meat, shellfish, and alcohol, can help decrease uric acid levels in the body, reducing the risk of gout attacks. Being low purine foods red onions and gout treatment is linked too often. They are extremely beneficial in reducing inflammation when consumed as salads.
2. Keep Yourself Hydrated

Drinking plenty of water can assist in flushing out uric acid from the body, reducing its buildup and the likelihood of crystal formation. Keeping your body hydrated all the time will not only keep you away from severe gout but it will keep you healthy and your metabolism going fast.
3. Manage Healthy Weight

Maintaining a healthy weight helps reduce the risk of gout attacks as obesity is linked to higher uric acid levels. So, a healthy mind should also adopt healthy lifestyle changes for healthy living to enjoy a better and healthier life every day.
4. Go For Herbal Remedies

Some herbs like turmeric and ginger are believed to possess anti-inflammatory properties that might help alleviate gout symptoms. However, consult with a healthcare professional before using any herbal remedies.
5. Rest And Elevation
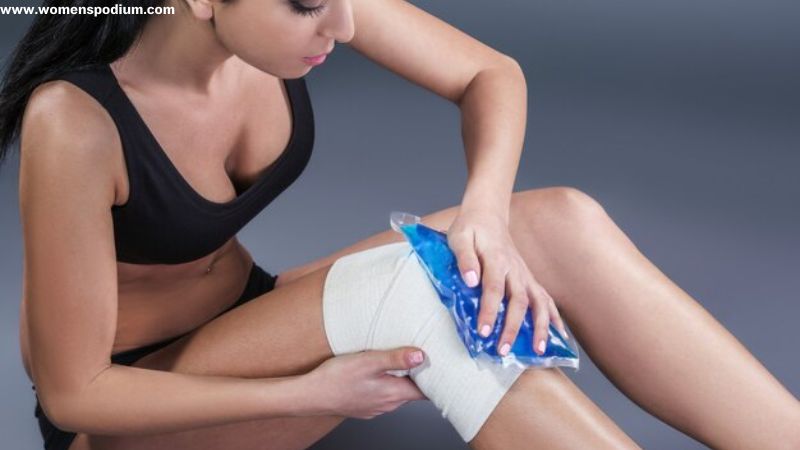

During a gout attack, rest the affected joint and elevate it to help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Applying ice packs or cold compresses to the affected joint can also help reduce swelling and ease pain during gout attacks.
6. Medical Treatments
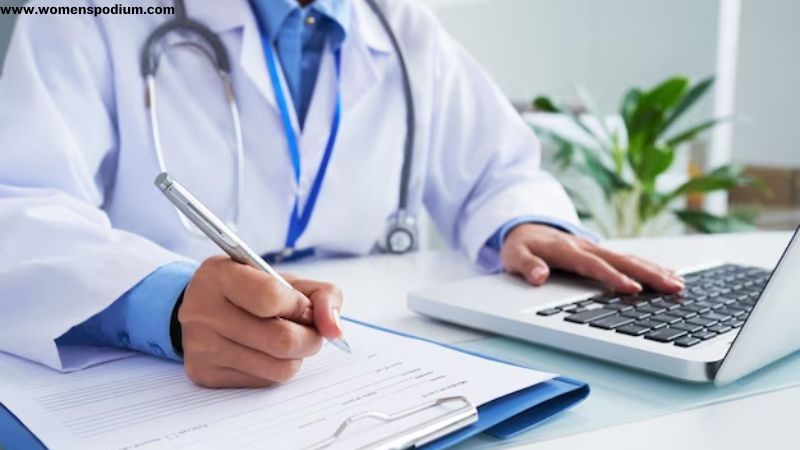

While avoiding foods bad for your health, you should also visit your physician and consult for some medications as well. Some beneficial medicinal treatment for gout includes; Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs), Colchicine, Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors, and Probenecid.
So, is gout an autoimmune disease? While gout involves an inflammatory response similar to autoimmune diseases, it is NOT classified as an autoimmune condition. Gout primarily stems from metabolic dysfunction leading to urate crystal formation. It distinguishes it from the autoimmune diseases involving the immune system’s attack on healthy tissues. Understanding the difference between gout and autoimmune diseases is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment of these health conditions.
Also Read: For people who are enjoying life and do not have any of such conditions, they should work on some tips to maintain fitness from the inside out to avoid conditions like gout.





